| Home | Report a Problem | Pollution Journal | Sewers & Drains | Our Sewage Works | Farm Run-Off | Invasive Species | How to Help | Who's Involved | River Facts | River Jargon |
www.RiverBollin.info
Macclesfield Waste Water Treatment Works
At the start of 2025, United Utilities are bringing on-stream an
innovative £50m water treatment process that will increase
the site's capacity to handle higher input flows from foreseeable
housing growth, and
will dramatically clean up the water discharged into the River Bollin.
In March 2024 members of the
Beacon group interested in improving the Bollin River were invited to see progress at the Prestbury site,
which also serves Macclesfield and Bollington, and to learn how it
works......

Work on the plant is driven by a requirement under the EU’s Water Framework Directive to reduce Phosphorus and Ammonia concentrations in discharges into the river.
Sewer overflow events lasting a few hours, are very much in the news, but a much bigger improvement to the Bollin water quality will result from the new treatment process putting cleaner effluent into the river all day, every day.
In March 2024 design work was at an advanced stage to add further storm tank capacity to accommodate forecast population growth as required under the Environment Act. This should reduce storm overflow spills from the works to less than 10 per year.
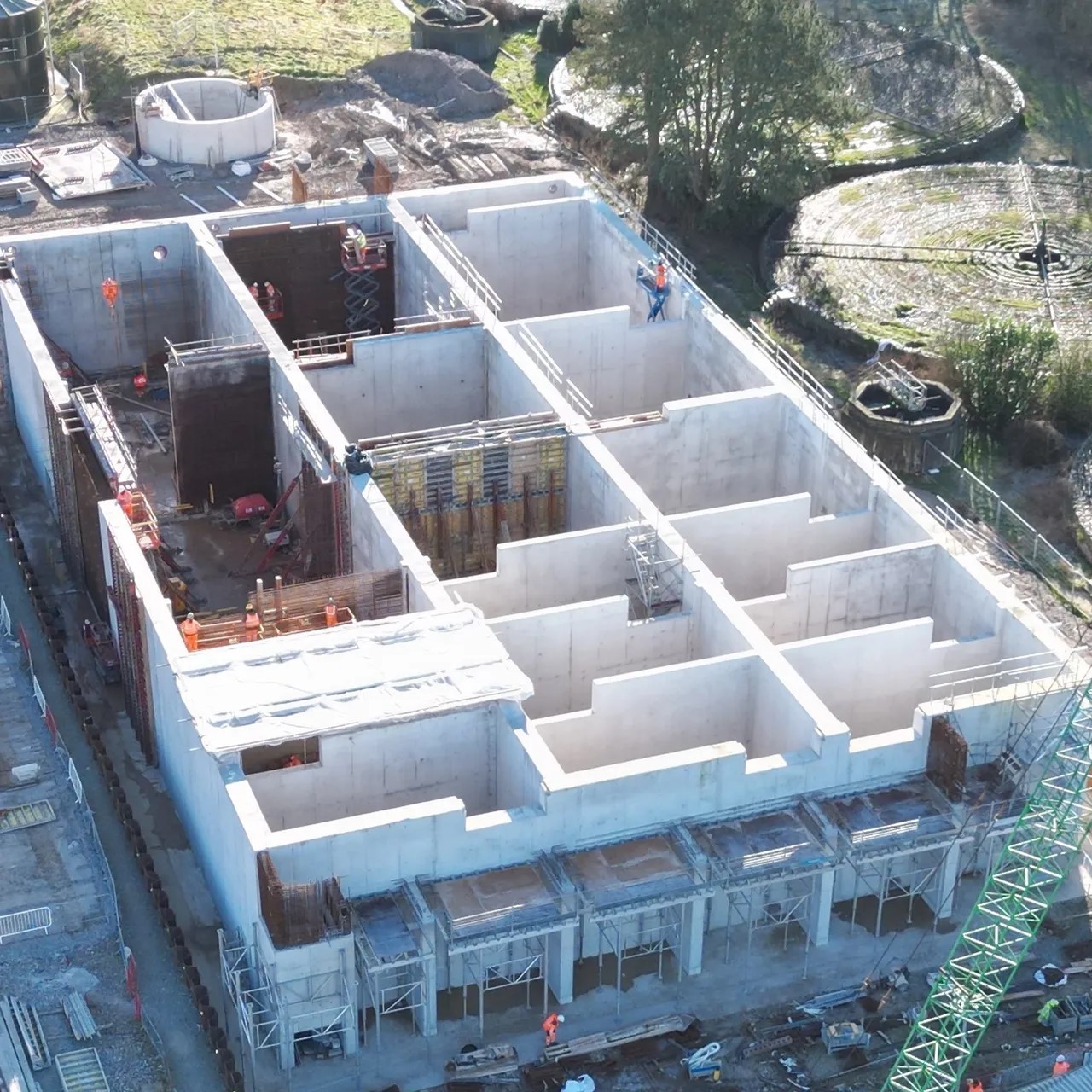
March 2024: the new concrete structure in the foreground above, is a four-channel inlet screen, with a fifth bypass channel. The white box-like structure in the distance is the new MOB (Mobile Organic Biofilm) plant.
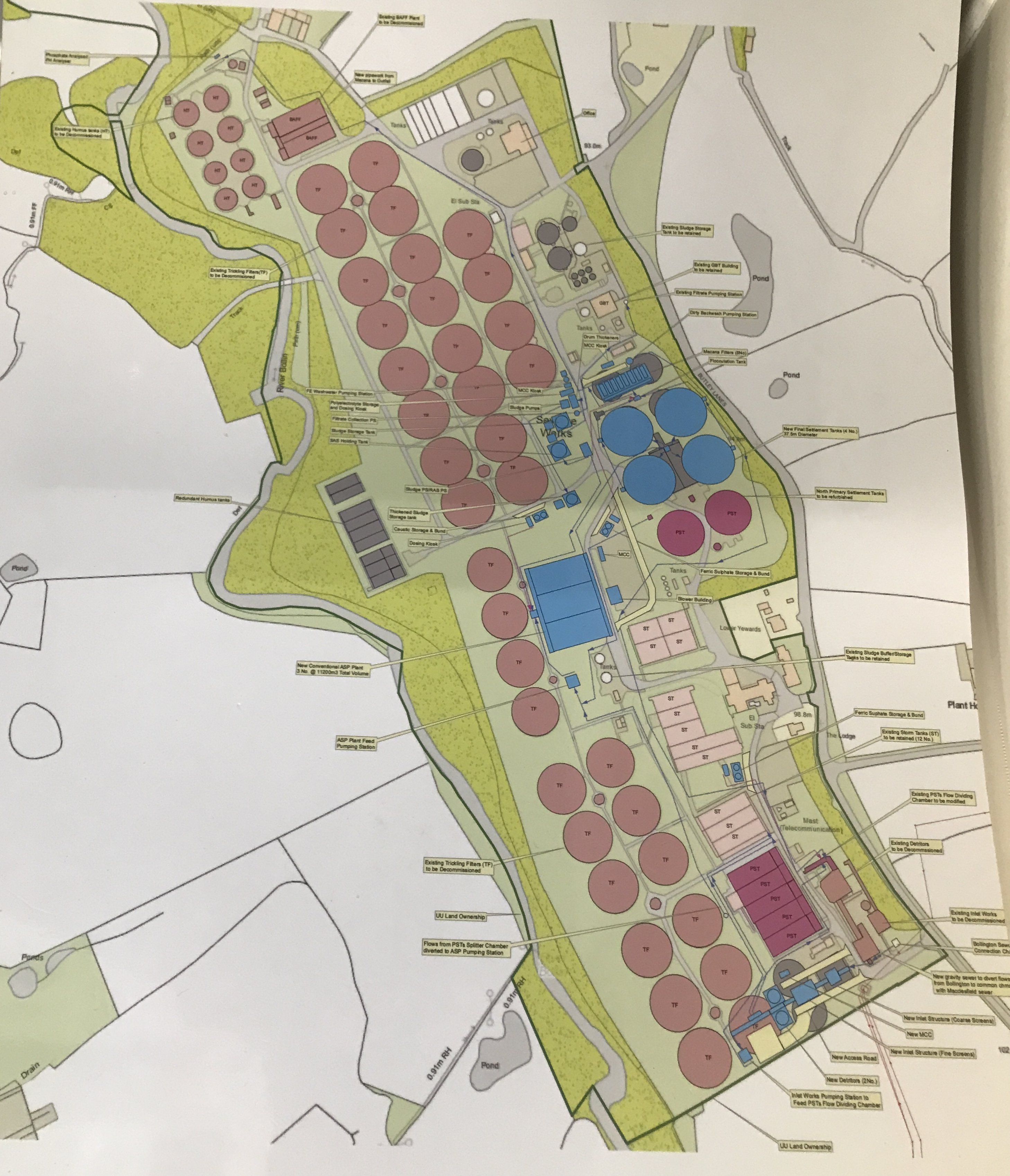
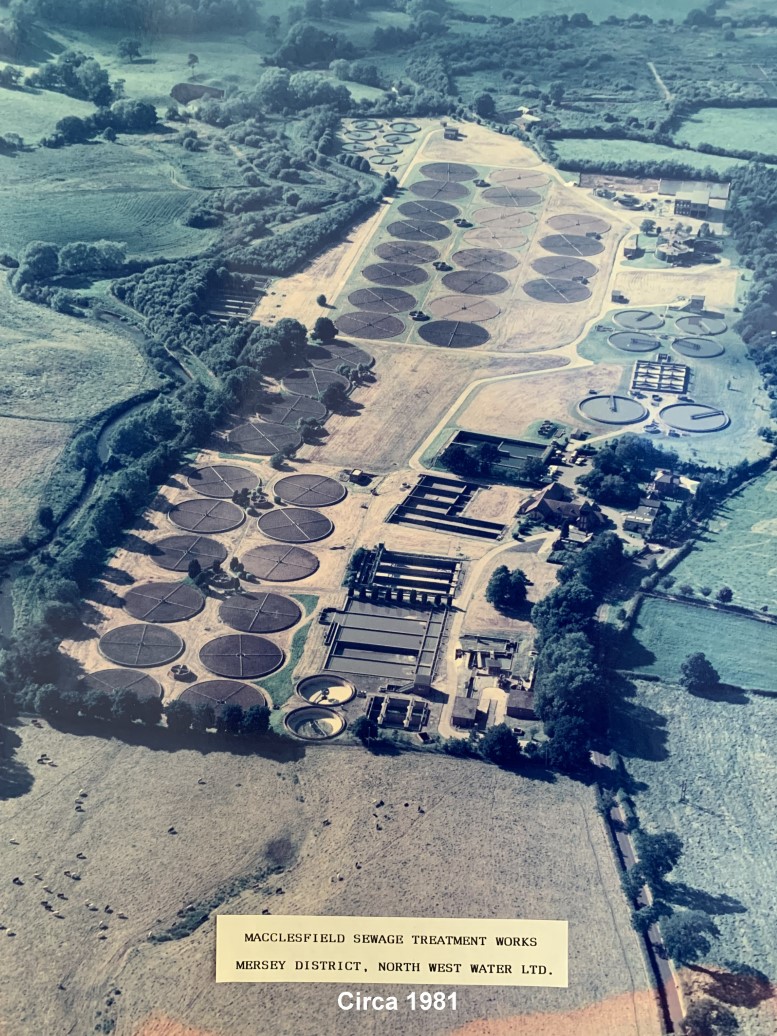
The works will make redundant the 36 circular biological filtering beds shown in pink on the plan below.
Some Statistics
The average person in the UK uses 142 litres of water each day; produces 0.4 kg (or 0.4litres) of faeces; and between 1 and 2 litres of urine. So around 2/142 = 1.4% of sewage is human waste. By the time this has passed down miles of sewer pipes, it arrives at the water treatment works mostly as a smooth watery sludge.
Heavy rain can more than treble the flow into the sewers, so by the time any Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) discharges into the river, the concentration of human waste is generally less than 0.5% - not as graphic as we might imagine, but enough to be a real health concern, and often only manifest by tampons and wet wipes appearing in the river. To make river users more readily aware of when a CSO might be discharging, the water companies have been obliged to publish almost live maps of the state of their CSOs here.
The North West of England has 40 per cent more urban rainfall than the industry average, and has 54% combined sewers - whereas the industry average is 33%.
How is the Sludge Cleaned?
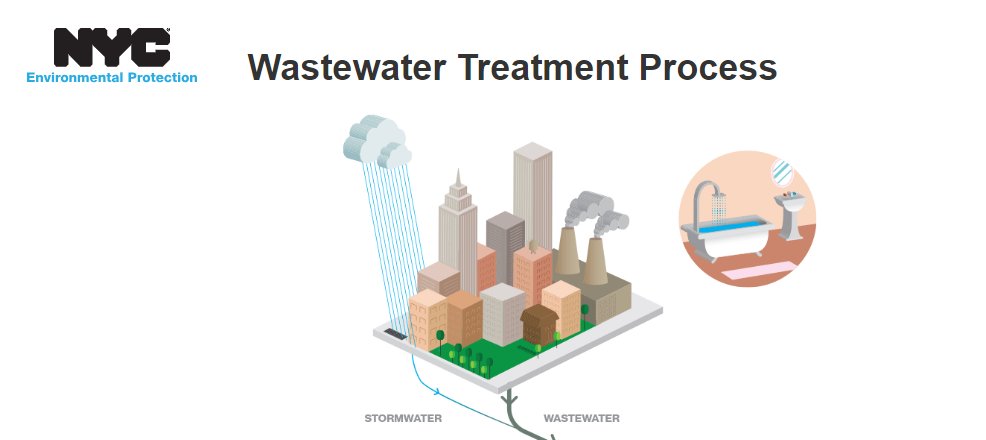
The basic process of water treatment is well illustrated in this description of New York city’s system:-
A principal aim of the waste water treatment process is to remove phosphates and nitrates. This is because, like farmyard manure, human waste has fertilising properties. If discharged into rivers it promotes excessive algal growth (eutrophication) which starves other water creatures of oxygen.
After initial sieving or 'screening' of the sludge to remove items larger than 6mm diameter, such as wet wipes and cigarette ends etc., the flow is slowed to allow settling out of grit (to avoid damaging the pumps). Grit is particularly found where there are combined sewers that collect sand and gravel from roadside storm gulleys.
 Incidentally,
attempts in recent years to promote the use of 'flushable' wipes have
now been abandoned and the 'Fine to Flush' approval has been withdrawn. All wipes are now identified as the principal source of
'fatbergs' blocking sewers - which of course trigger overflow
discharges into rivers.
Incidentally,
attempts in recent years to promote the use of 'flushable' wipes have
now been abandoned and the 'Fine to Flush' approval has been withdrawn. All wipes are now identified as the principal source of
'fatbergs' blocking sewers - which of course trigger overflow
discharges into rivers.
The sewage is then aerated or 'activated' by bubbling air through it to help bacteria convert urea into nitrates.
This is followed by an ‘anoxic’ section, depleted of oxygen, where a different strain of bacteria
have to get their oxygen by stripping O2 molecules from the nitrates
- a process
which releases nitrogen as a gas.
(Link
to a brilliant explanation of this process).
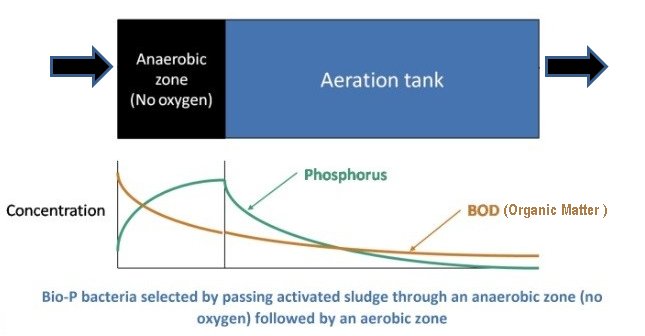
Paradoxically, in the absence of oxygen, phosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) consume organic matter, and release more phosphates into the water.
However, if the water is subsequently aerated, the same PAOs consume even more phosphates than they produced.
In subsequent clarification tanks, the organisms sink to the bottom where they can be collected in the sludge and removed, taking the phosphorous with them. Source
Some of the sludge is collected and shipped off site for digestion to produce methane gas as a fuel, or dried and used as an agricultural fertiliser. But some of the sediment is pumped back into the first aeration section to increase the active bacteria concentration by up to perhaps 30 times the original incoming sewage levels.
The Equipment
The incoming sewage or 'influent' is first sieved or 'screened' by a two stage process that removes everything larger than 6mm in diameter.
The new structure has four parallel paths and a fifth emergency bypass channel.
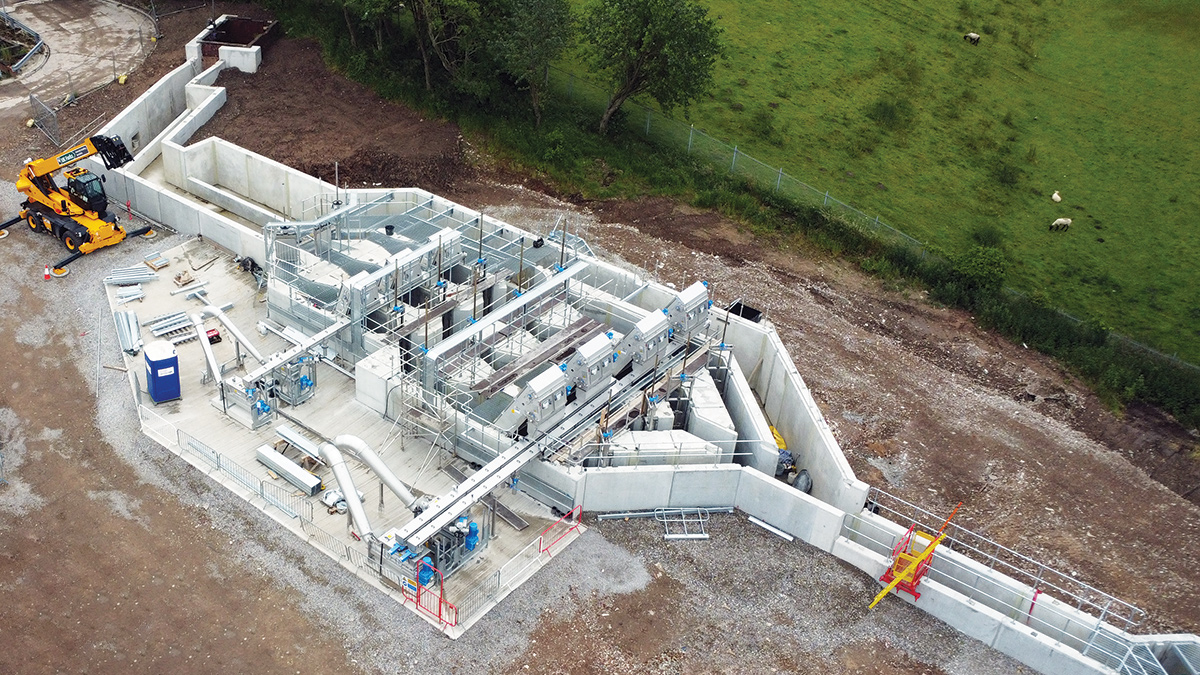
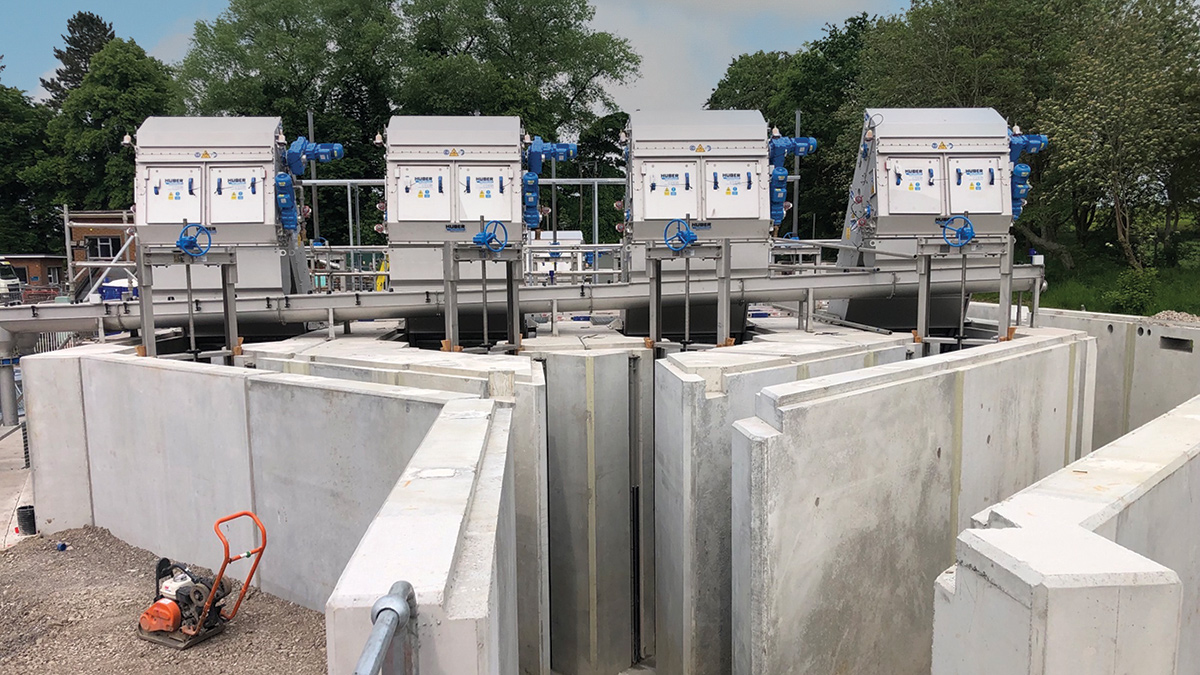


Circular Tanks
There are two types of circular tank visible on the Prestbury site; one type full of water, and one type full of gravel.
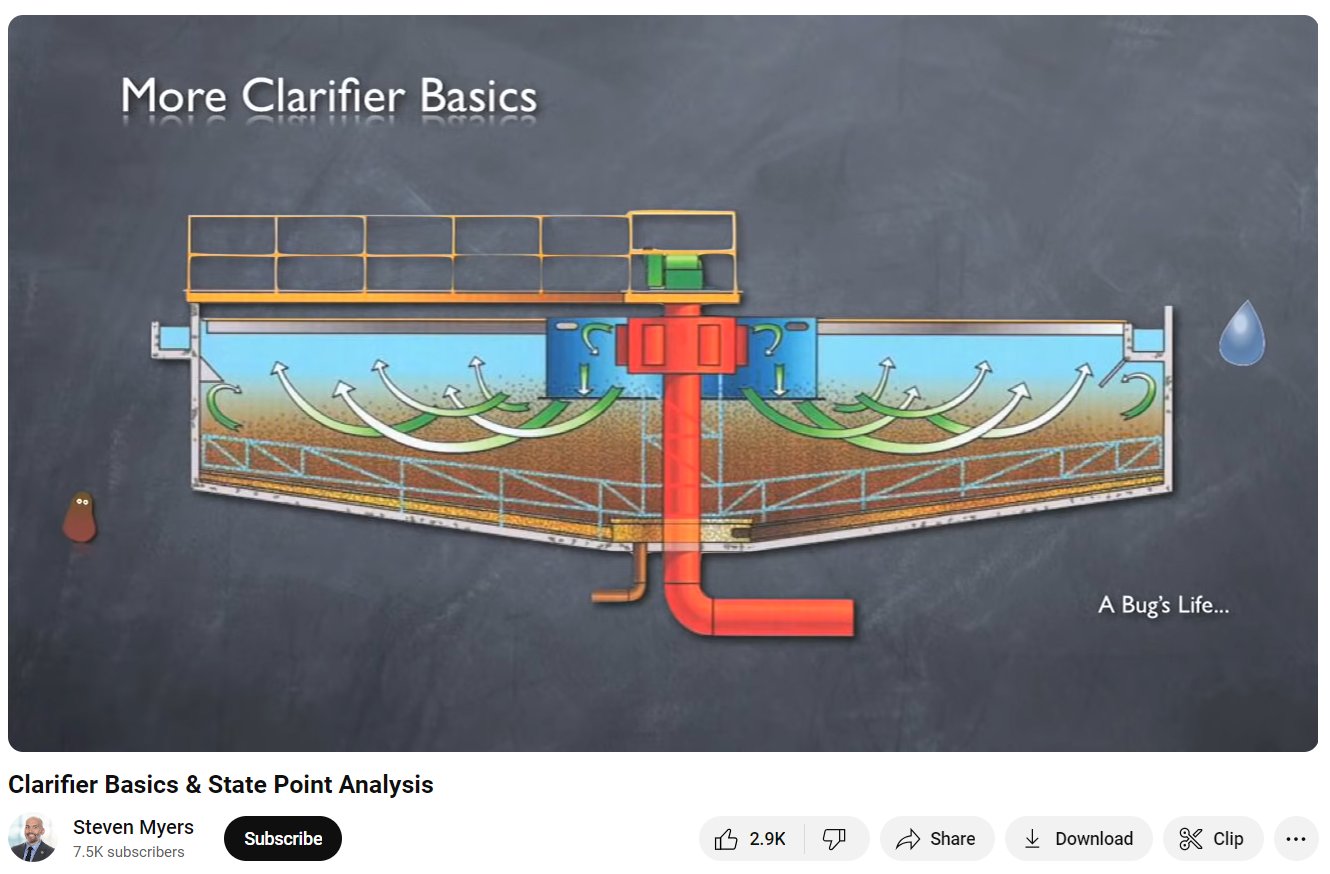
Water-filled Clarifiers allow time for solids to separate from clearer water:-

A motorised wheel running around the perimeter slowly drives the bridge around, taking with it a sludge scraper on the floor of the tank.
Watch the first 2 minutes (only) of this clarifier animation
The bridge also carries around a scum-removing blade at the surface:-
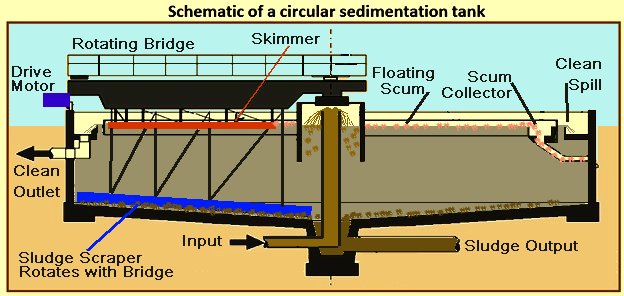
Cleaned water passes under the scum retaining ring and spills over the edge of the tank.
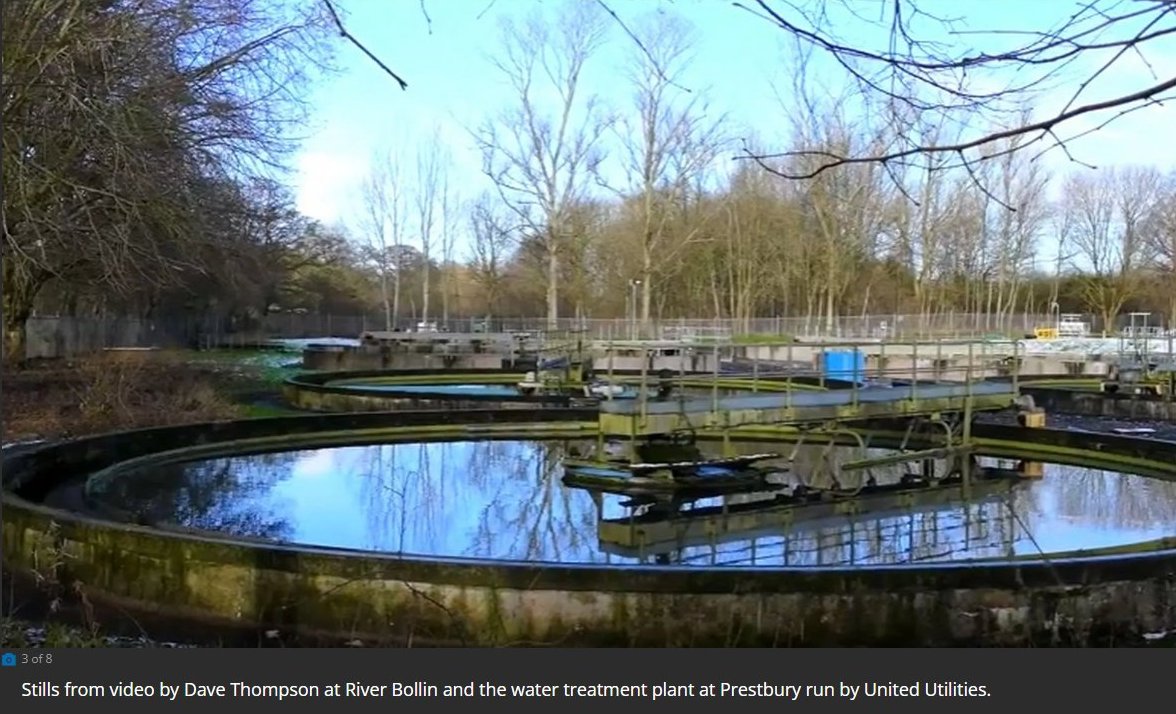
Gravel-Filled Trickle Filters
The clarified water is trickled over a bed of gravel where bacterial activity further cleans the water.
The arms are propelled simply by the thrust of the water flow. There
are around 36 of these filters on the site, and all will be made
obsolete by the new MOB plant described below.

Aeration and Activation
Over the years, the activation of sludge by bubbling air
upwards through it has been enhanced by adding plastic substrates on
which the bacteria can grow:- sometimes in sheet form, vertical tubes, or honeycomb-cored plastic chips.
The honeycomb offers a large surface area for bacterial growth.
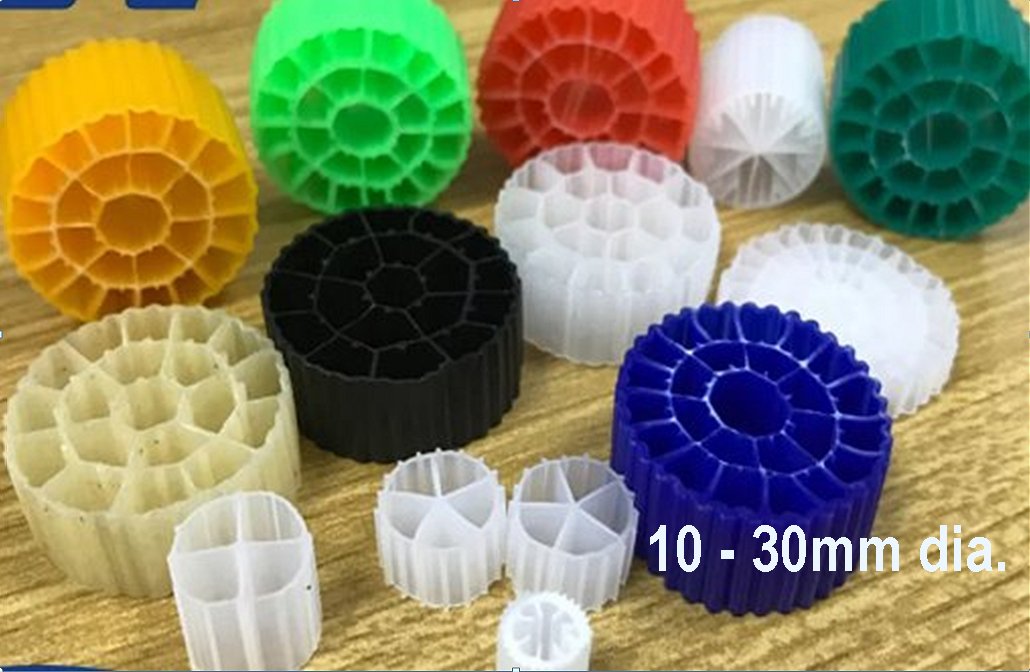

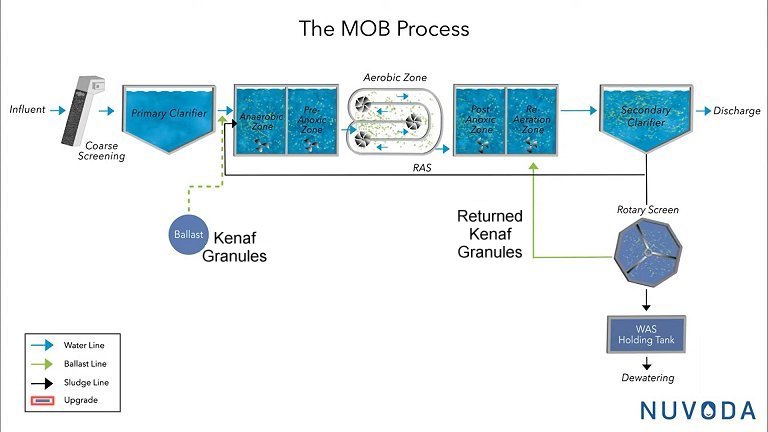
The Prestbury site will be the first in the UK to use the new Novoda Mobile Organic Biofilm (MOB) system which effectively miniaturises this honeycomb chips idea, using approximately 1mm diameter granules milled from a hemp-like crop called Kenaf as ‘the ballast’.
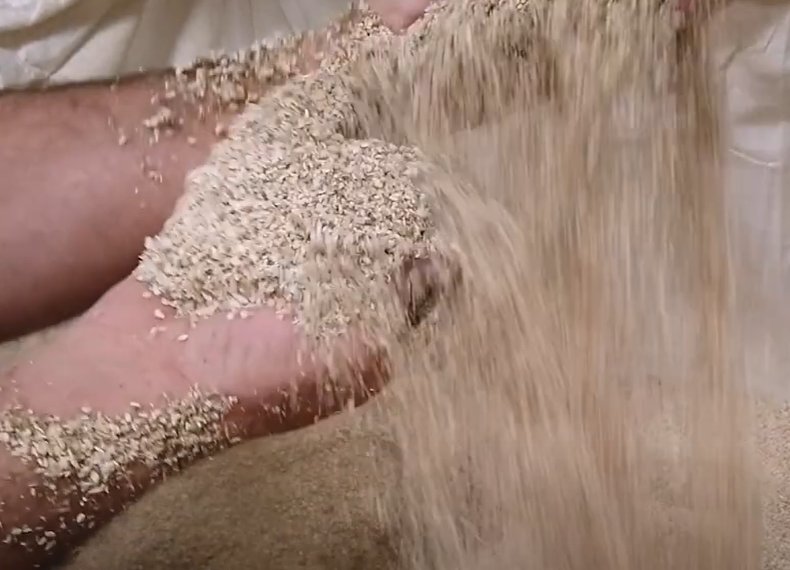

Like the plastic chips, the Kenaf granules also have a honeycomb structure - but on a tiny scale. When the granules are added to the incoming ‘influent’ liquid sludge, a porridge-like consistency is achieved.
The outer layers of the granules host aerobic bacteria, and the inner surfaces are largely anoxic, promoting nitrogen release and phosphate digestion.
After passing through a series of alternate aeration and settlement processes, bacteria are detached from the exterior of the Kenaf granules in a rotating screen, (not unlike a huge tumble-drier drum).
(Bearing in mind that the granules themselves are approximately 1mm diameter, the detached sediment particles are tiny.)
After screening, the ‘cleaned’ ballast granules are then pumped back into the process. The granules are so durable that only around 2% need replacing per year.
This new process is so effective; all of the trickle filters at the Prestbury site will become redundant.
The MOB tank under construction, showing three parallel lanes each of seven stages. Courtesy of Offa-Fix. See gallery.
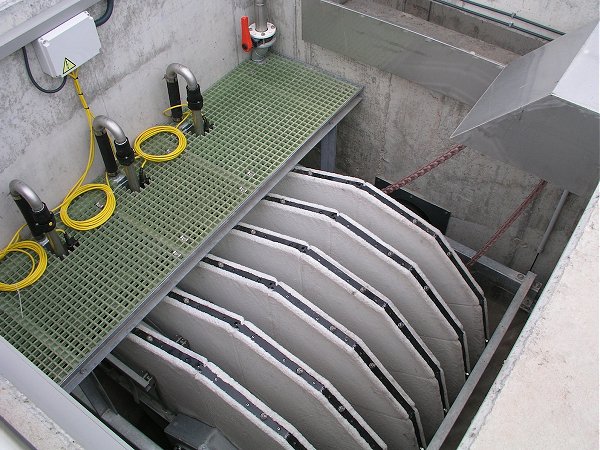
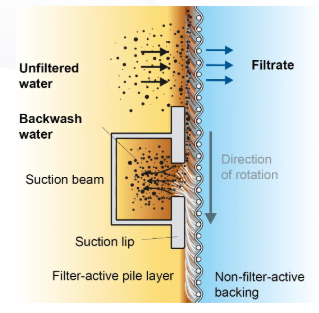
The new final treatment station will utilise four Mecana tertiary pile cloth filters (TPCFs) for solids removal.
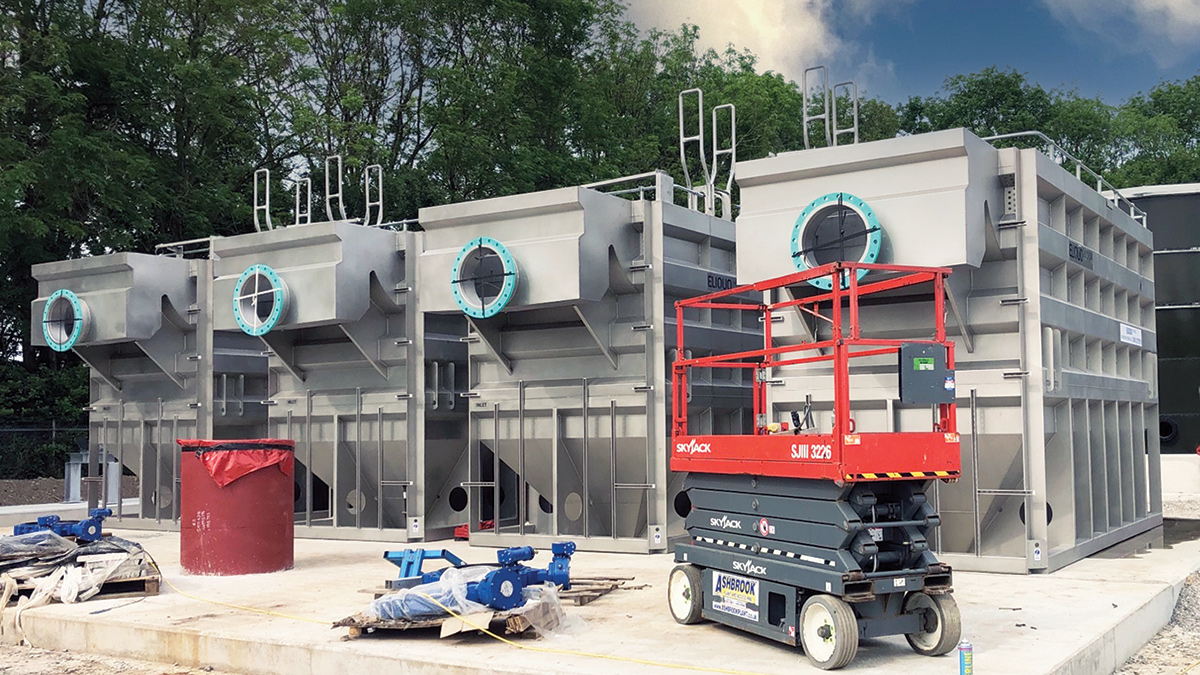

A moving textile disc has a pile that is flattened by the flow, retaining particles until the disc passes a short reverse-flow section that sucks away the particles.
Two discs are placed back to back and the cleaned water is drawn out of the enclosed space.

Review of the Prestbury project status July 2024 by 'Water Projects'.
What Happens to the Sludge?
Sludge treatment involves removing the water from the sludge to reduce its weight and volume. This process produces methane gas which can be used to generate renewable electricity.
Nationally, around 87% of treated sludge is recycled to agricultural land as a soil improver where it forms an important source of nutrients and organic matter for growing crops. There are strict quality standards that must be adhered to for the production of biosolids.
Of the remaining 13% of treated sludge, 4% is incinerated, 3% is used in industry (typically as a fuel for cement production) and 6% is used in land reclamation.
The main objective of sludge treatment is to create a biosolids product that is safe and acceptable to recycle to agriculture. This includes reducing or eliminating potentially harmful micro-organisms e.g. E. Coli and Salmonella spp. and reducing the fermentability of the final biosolids to acceptable levels.
Various treatment technologies are employed to produce biosolids; about 73% by anaerobic digestion and 22% by lime stabilisation.
from Southern Water on Vimeo.
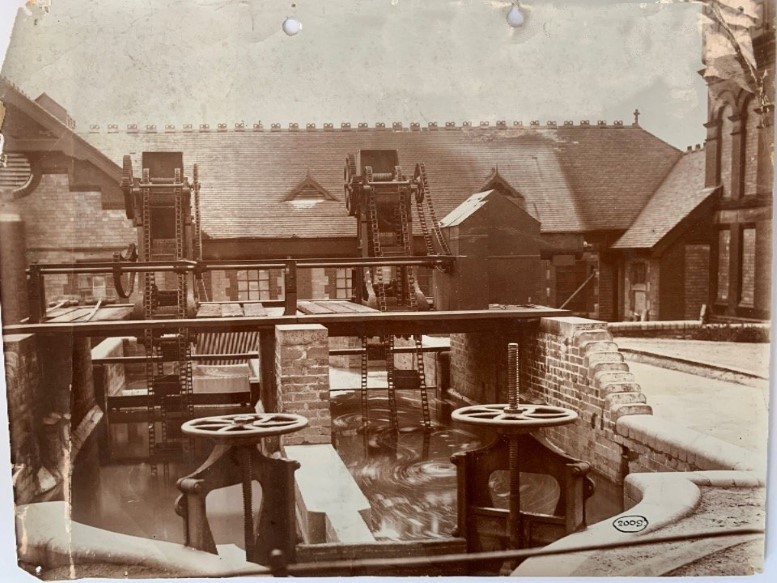
A Little History:
The waste water treatment works at Prestbury was first proposed in 1880 and was opened in 1907. The site was chosen because sewage could flow downhill from Macclesfield, Bollington and Prestbury.
By 1935 the present day storm tanks were in use.
There appears to have been significant investment around 1975 with a new inlet works, treatment processes including some sludge treatment.
Further improvements were made in 1990, including new settlement tanks, and the BAFF (Biological Aerated Flooded Filter) plant went in around the turn of the century.
The
activated sludge process described above was developed in 1913 by two engineers, Ardern and Lockett, at the Davyhulme Sewage Works, Manchester.
This was of course just too late for the Macclesfield works, and it
was 1920 before Sheffield became the first UK city to fully apply the
active sludge process.
This approach quickly spread worldwide, becoming the standard for sewage treatment…………









Some Interesting Links
Open University: a 7 min summary of waste water treatment from 2011
United Utilities' update video on the Prestbury Works March 2024
United Utilities: A History of Water Treatment
A 3D Virtual Tour of a waste Water Treatment Plant
The History of Water Treatment from 3,500 BC to the 1990s
Microbes in Sewage Treatment - Open University
(as used by UU in Kendal, Morecambe, Failsworth and Blackburn )You may want to fast-forward the video to 4 mins.
Lutra's video of the MOB process
Lutra TV:
'The YouTube Channel for Water & Wastewater Professionals'
December 2024 Press Release
| Back to Main Page |